The construction industry, long dominated by traditional, analog processes, is rapidly embracing the digital era. Over the past decade, advanced technologies have redefined how firms plan, collaborate, and manage projects — leading to smarter workflows, improved safety, and reduced costs.
Among these innovations, Building Information Modeling (BIM) stands out as a transformative tool that allows teams to visualize, simulate, and manage construction projects in digital form. Yet, to fully unlock the potential of BIM, accurate and timely data is essential — and this is where drones (UAVs) play a crucial role. Together, BIM and drone technologies form a powerful synergy that drives precision, transparency, and efficiency on today’s job sites.
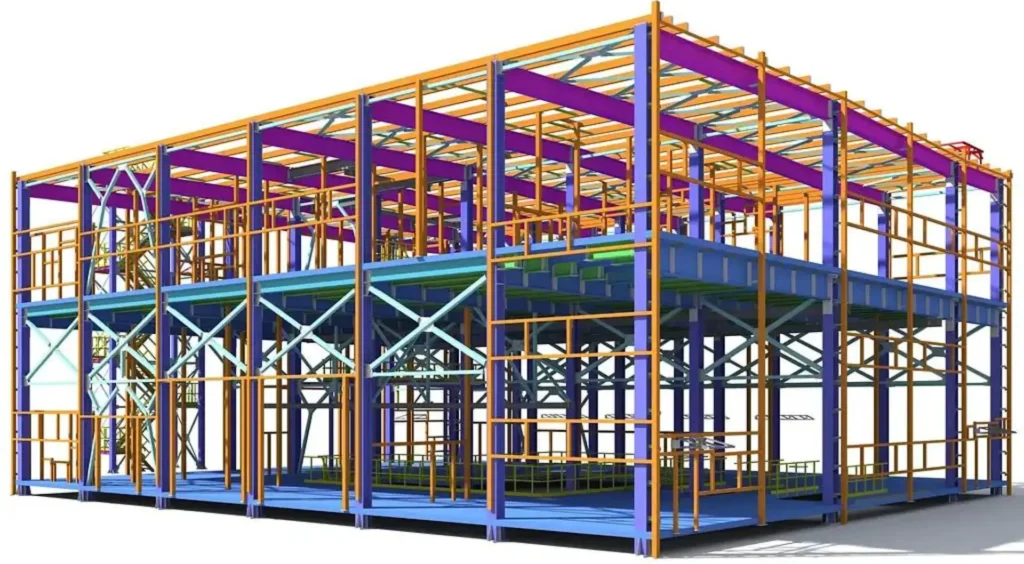

Building Information Modeling is far more than a digital version of a blueprint. As defined by ScienceDirect, BIM is a collaborative process that enables stakeholders to share and manage data throughout a project’s lifecycle — from initial design to construction and beyond.
At its core, BIM creates a 3D digital representation of a structure that includes not only geometry but also information about materials, schedules, and costs. This digital twin acts as a single source of truth, allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to access real-time information on project status, design changes, and resource allocation.
Beyond visualization, BIM platforms serve as collaborative workspaces where stakeholders can log updates, make design annotations, and monitor progress remotely. For BIM to remain truly effective, however, it requires constant input of accurate, real-world data — a task ideally suited for drones.
Drones have rapidly become indispensable tools in construction. Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and LiDAR modules, UAVs can capture high-resolution aerial data to generate detailed 3D models of job sites.
By integrating drone-derived data into BIM platforms, teams can:
Two key drone-based methods enable this integration:
Photogrammetry — creating 3D models from overlapping 2D images, a process simplified by functions like Smart Oblique Capture available on drones such as the DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise and Matrice 350 RTK with Zenmuse P1.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) — using laser pulses to map surfaces with centimeter-level accuracy, even in low-light or obscured environments on drones, such as DJI Matrice 350 RTK with LIDAR L2.

There are a number of key areas where drones make the BIM process easier, safer, and more efficient — from pre-construction planning to post-completion inspections.
1. Conducting Structural Inspections Without Human Risk
Structural inspections are among the most dangerous tasks in construction and demolition. Drones can safely perform these inspections from the air, eliminating the need for human workers to access hazardous areas and reducing risk on-site.
2. Pre-Construction Site Inspections and Analysis
Before construction begins, drones can survey and map the terrain, capturing detailed imagery and elevation data. This allows architects and engineers to create more accurate BIM drawings and identify potential challenges such as uneven ground or drainage issues — long before construction starts.
3. Advanced Point Cloud Scanning
Using LiDAR or photogrammetry, drones can capture high-density 3D point clouds with exceptional accuracy. Compared to traditional ground-based scanning, drone-based scanning offers a faster, more comprehensive aerial perspective — providing a clear understanding of site topography and spatial relationships.
4. Aerial Photography and Progress Tracking
Throughout the construction phase, drones can take periodic aerial photographs to update BIM models and project records. These visuals not only enhance project documentation and investor reporting but can also serve as powerful assets for marketing and client communication.
5. Monitoring Site Activity and Ensuring Safety
Frequent drone flights offer management a real-time view of site activity, helping identify bottlenecks or unsafe conditions early. This situational awareness contributes to improved safety compliance, site organization, and workflow coordination.
6. Project Completion Checks and Quality Assurance
Even after a project is completed, drones continue to add value through final inspections and thermal imaging. Thermal sensors can detect temperature anomalies, identifying areas of heat loss or insulation failure — valuable insights for assessing a building’s energy efficiency and structural soundness.
7. Meeting Government and Regulatory Requirements
Many projects require documentation for compliance and inspection purposes. Drones enable faster, more accurate data capture — from as-built verifications to environmental compliance — allowing contractors to meet regulatory standards efficiently and provide authorities with verifiable digital records.
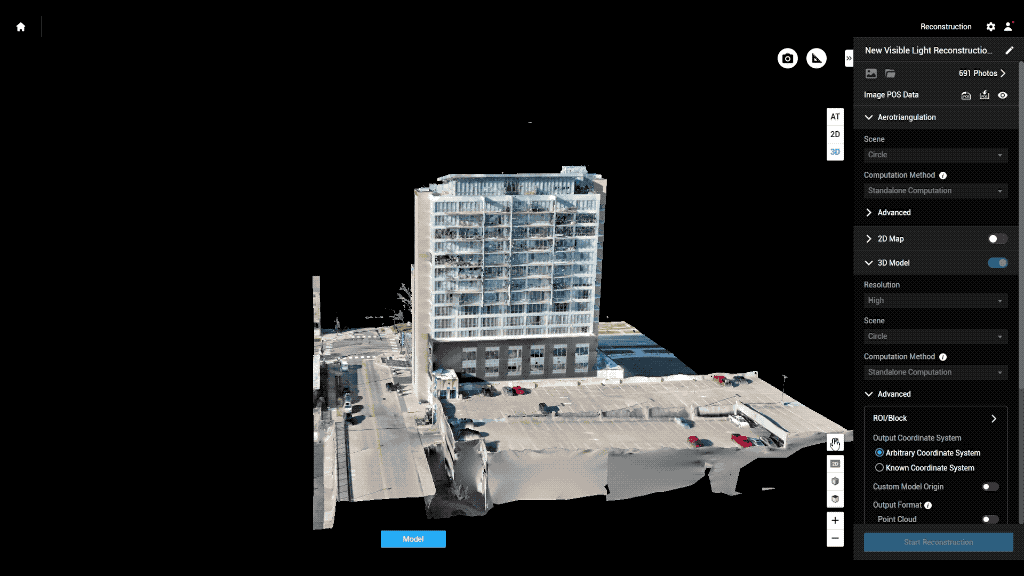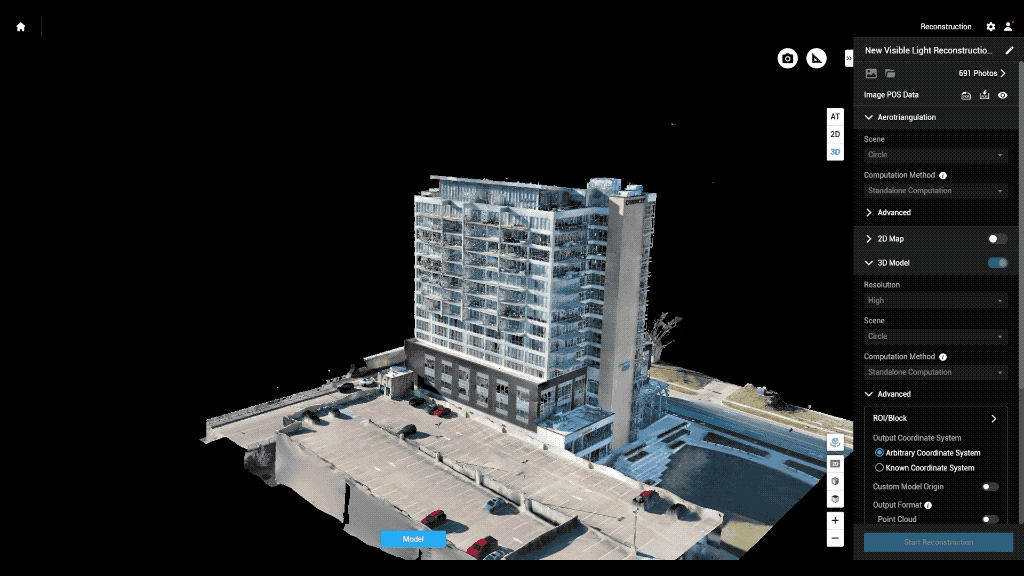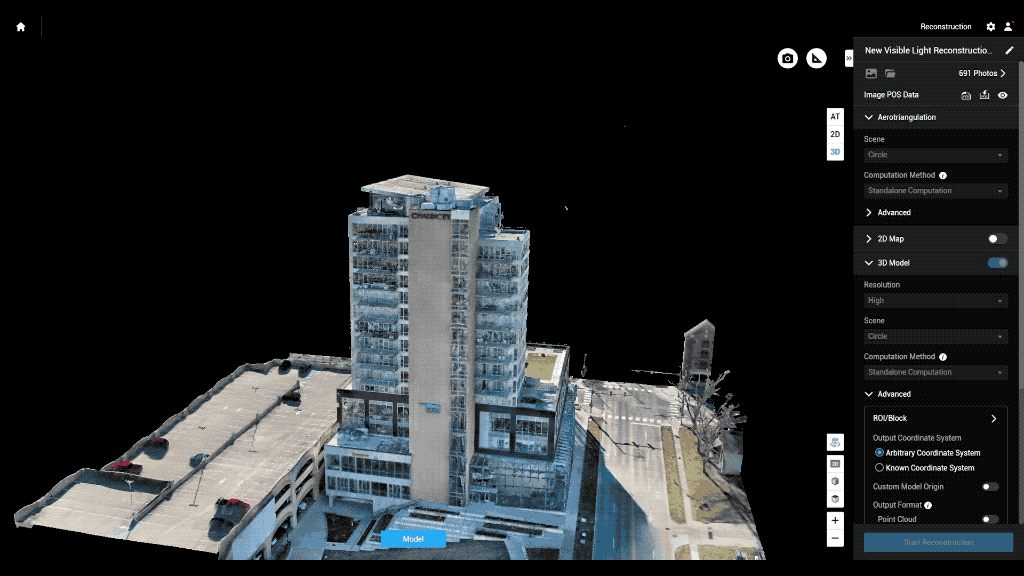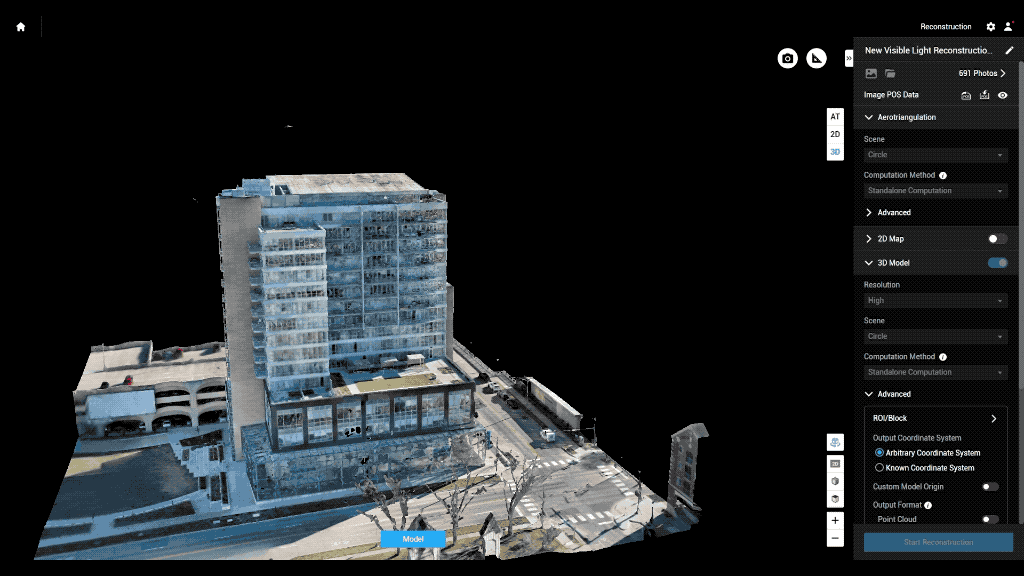
Drones enhance BIM at every stage of a project — from planning and execution to post-construction inspection and maintenance.
Before Construction: Site Surveying and Planning
Drones conduct precise topographic and terrain surveys, capturing elevation data and site conditions that feed directly into BIM models. This ensures planning begins with accurate ground truth data, reducing rework and design errors later.
During Construction: Monitoring and Progress Tracking
Regular drone flyovers provide updated 3D maps and orthomosaics, allowing teams to overlay real-time data on BIM plans. This helps identify discrepancies, monitor productivity, and manage site logistics, such as material placement or equipment utilization.
After Construction: Inspection and Facilities Management
Even after completion, drones continue to deliver value. UAVs perform maintenance inspections, capturing detailed imagery and point clouds for ongoing facility management — ensuring safety, compliance, and structural integrity.

Combining drones with BIM technology yields measurable returns across cost, time, and quality dimensions.
Enhanced Decision-Making: Frequent drone surveys ensure BIM models reflect current site conditions, enabling contractors to adjust plans in real time.
Unmatched Accuracy: With Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning, drones achieve centimeter-level precision, supporting detailed measurements and quality control.
Improved Oversight: Drone aerial data offers a comprehensive “bird’s-eye view” of the site, helping managers track assets, monitor safety compliance, and maintain project timelines.
Ultimately, this integration drives data-driven decision-making, minimizes delays, and reduces costly rework, leading to higher efficiency and profitability.
Selecting a suitable drone depends on project requirements, budget, and the type of data needed.
Recommended options include:

These platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with BIM workflows, offering reliability, versatility, and the level of detail demanded by modern construction standards.
BIM and drone technologies represent a powerful convergence of data and design — transforming how construction firms plan, build, and manage infrastructure. Drones serve as the eyes of BIM, providing the real-time, high-precision data that drives informed decision-making at every stage of the project lifecycle.
For contractors seeking to enhance project visibility, accuracy, and collaboration, integrating drone technology into BIM workflows is no longer optional — it’s essential for staying competitive in the modern construction landscape.