
In the rapidly evolving world of geospatial technology and digital infrastructure, drones have redefined how professionals collect, process, and interpret data. We have discussed this transformation with Riyadh Ashoor, Operations Manager, UAV & ROV Technologies from Muscat, Oman, whose hands-on experience with drone deployment spans construction, energy, and environmental sectors. In this interview, he shares his journey, insights, and vision for the future of drone technology in industrial and infrastructure applications.
Riyadh’s introduction to drones began in 2016 while working at a landfill site. Driven by the need to improve volume calculations through 3D modeling, he decided to experiment with drone mapping — despite multiple initial failures. “I saw the need to have a 3D model and use it for volume calculation,” he recalls. “After many failed trials, I finally succeeded. From that day, I began using drones across many different services.”
What started as a problem-solving solution quickly grew into a professional passion. Riyadh has since integrated drones into diverse applications — from surveying and mapping to inspection and environmental monitoring — transforming how projects are executed in Oman and beyond.
Before the integration of drones, many field operations relied on manpower-intensive workflows, heavy logistics and site shutdowns. Today, Riyadh’s teams achieve in minutes what previously required days.
“Now, with drone-based systems, we can collect accurate spatial data in minutes with minimal disruption,” he explains. “The integration of tools enables us to automate workflows — from flight planning to data visualization — improving project turnaround time by more than 60% while maintaining centimeter-level accuracy.”
This efficiency not only streamlines operations but also enhances worker safety and decision-making.

According to Riyadh, the most significant advantages of drone technology are precision, safety, and scalability. Drones can access remote or hazardous areas, reducing the need for human presence in risky environments, while producing high-resolution data that traditional methods can’t match.
However, challenges remain. “Each project must comply with Civil Aviation Authority permits,” he notes. “Integrating large data sets into existing client systems sometimes requires custom cloud or on-prem solutions — especially for governmental organizations where data sovereignty is critical.”
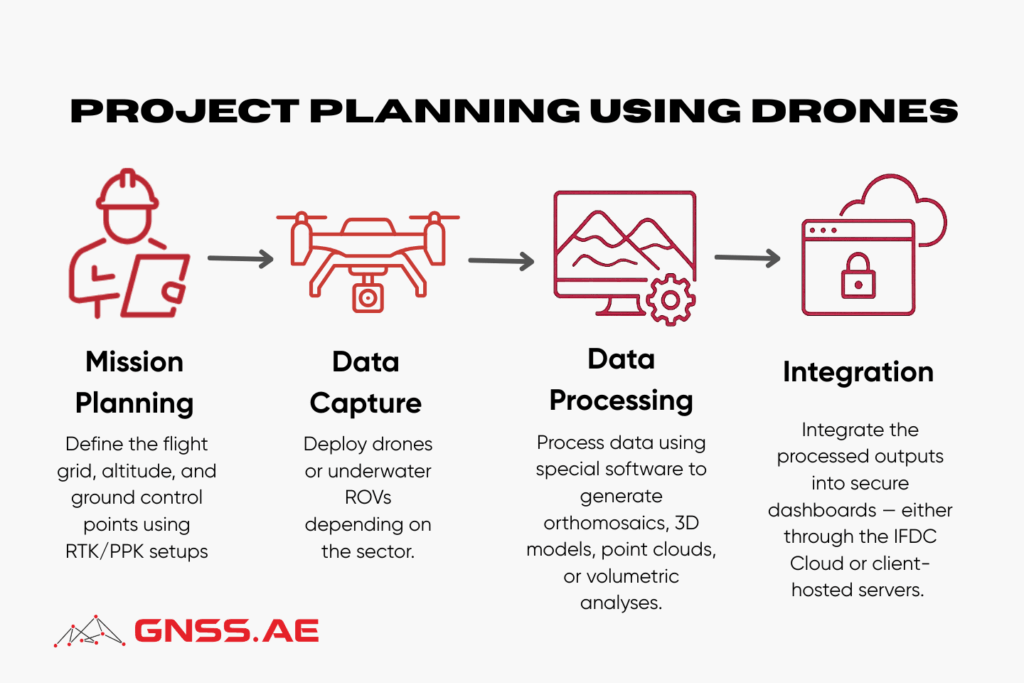
Riyadh’s team follows a structured and efficient process for every drone operation, from mission planning to final data delivery. “Our workflow begins with a mission planning phase, where the team defines the flight grid, altitude, and ground control points using RTK/PPK setups,” he explains. “During data capture, we deploy drones or underwater ROVs depending on the sector. Once the data is acquired, it’s processed using special software to generate orthomosaics, 3D models, point clouds, or volumetric analyses.”
The processed outputs are integrated into secure dashboards — either through the IFDC Cloud or client-hosted servers — allowing real-time analysis and faster decision-making for inspection and engineering teams.
For Riyadh, the most exciting developments lie at the intersection of drones, AI, and cloud analytics. “Every dataset we capture is a story waiting to be told,” he says. “Whether it’s monitoring coastal erosion, detecting methane leaks, or mapping solar farms, drones are becoming intelligent agents — not just data collectors.”
He envisions a future where drones, powered by machine learning and computer vision, operate autonomously, identify faults in real time, and support predictive environmental monitoring. “The potential for autonomous docking, AI-based fault detection, and environmental forecasting truly inspires me,” he adds.
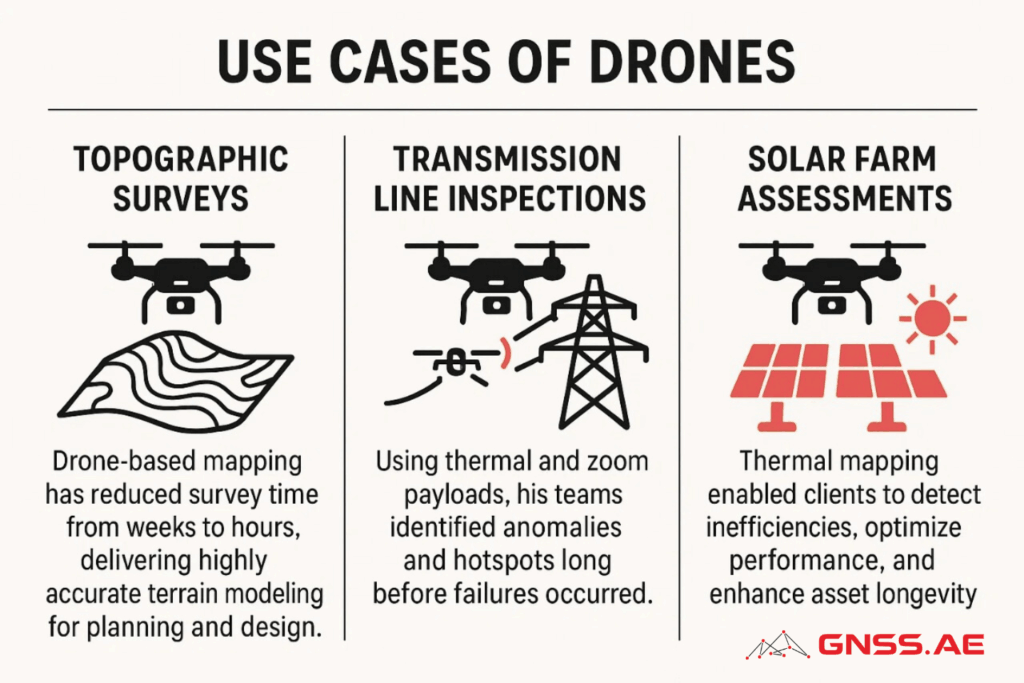
Riyadh’s projects have demonstrated tangible impact across sectors including construction, energy, water, oil and gas, and telecommunications.
“The results consistently show higher safety, faster delivery, and smarter decision-making powered by visual intelligence,” Riyadh emphasizes.
Riyadh sees drones evolving from operational tools to fully integrated digital assets, forming part of a larger ecosystem linked through IoT, AI, and cloud connectivity. This vision aligns closely with Oman’s national innovation and digital transformation goals.
“The next phase for my company involves many new solutions and cross-sector integration with Oman’s vision,” he shares. “We’re also focusing on training and knowledge transfer, ensuring Oman’s next generation of engineers and operators can carry this innovation forward.”
Drone technology is at the forefront of digital transformation across multiple industries — redefining how organizations collect, analyze, and act on spatial data. What once required extensive manpower and costly logistics can now be achieved in minutes through intelligent aerial systems that deliver centimeter-level precision.
As drones continue to merge with AI, IoT, and cloud computing, they are evolving from simple data acquisition tools into autonomous platforms capable of real-time analysis, predictive insights, and seamless integration with enterprise systems.