How can cities optimise infrastructure? How do businesses understand customer behaviour through location data? How can governments map and respond to disasters more effectively? For all these questions, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide the foundation.
GIS is an essential technology that transforms spatial data into meaningful insight, supporting decision-making, improving operational efficiency, and driving innovation across countless industries. From risk assessment to site optimisation, GIS offers endless possibilities for understanding and improving the world around us.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are specialised computer systems designed to capture, manage, analyse, and visualise location-based—or geospatial data. Whether mapping objects on the Earth’s surface, analysing population trends, or modelling environmental risk, GIS provides the framework that connects complex datasets with geographic context.
Rooted in the principles of cartography, GIS goes beyond traditional mapmaking. It brings together digital representations of the Earth and advanced analytical tools, allowing users to understand relationships, patterns, and changes across both two-dimensional and three-dimensional environments.
The purpose of GIS is simple yet powerful: to enable better decision-making by understanding how geographic factors influence people, places and events.
A modern GIS integrates several essential components that work together to deliver accurate and actionable results:
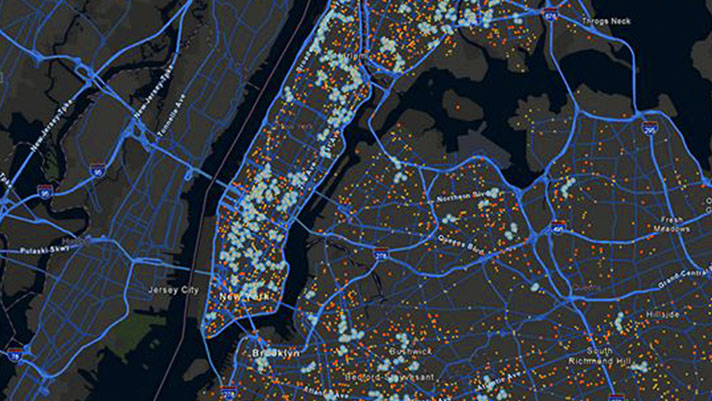
GIS is one of the most versatile technologies used today. Nearly every industry relies on geographic data to make informed decisions. Below are some of the most impactful applications:
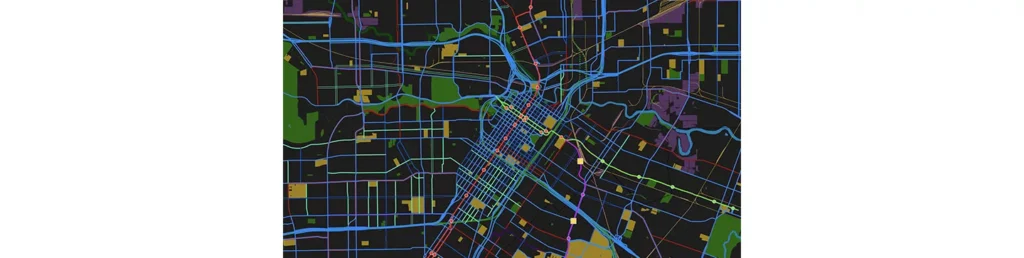
GIS is not just a mapping tool—it’s a strategic asset that empowers industries to operate more efficiently and make better decisions.
GIS mirrors the way we naturally think and make decisions spatially. Whether choosing the closest restaurant or identifying the fastest delivery route, spatial thinking is part of everyday life.
For businesses, GIS elevates this intuitive process into advanced analytical capabilities:
Finding the best store locations based on traffic, demographics, or land availability
Combining census data with geographic boundaries to create market and thematic maps
Understanding customer distribution, spending patterns, and regional behaviour
GIS allows organisations to merge tabular data (e.g., demographics, income, sales) with location information, creating powerful thematic maps that guide strategic planning, marketing, and resource allocation.

GIS has become indispensable across both public and private sectors. Examples include:
Retailers – selecting store locations
Insurance companies – underwriting and risk evaluation
Banks – customer targeting and service planning
Logistics companies – fleet routing and delivery optimisation
Utility providers – monitoring smart sensors and preventing outages
Government agencies – urban planning, tax management, and public services
Public safety – fire and police departments deploying resources efficiently
From global enterprises to local governments, GIS supports smarter planning, safer communities, and more efficient operations.
Enhanced Decision-Making
GIS visualises complex datasets, helping decision-makers identify patterns and relationships that are difficult to see in traditional reports.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Route optimisation, resource management, and automated workflows reduce time, cost, and manual effort.
Significant Cost Savings
Whether reducing delivery mileage, optimising infrastructure investments, or preventing service disruptions, GIS drives measurable financial impact.
Better Risk Management
Real-time spatial analysis supports emergency response, asset protection, and disaster mitigation.
Deeper Customer Insights
Businesses gain a clearer understanding of market demographics, customer movement, and geographic trends.
Sustainability & Environmental Protection
GIS supports conservation efforts, climate monitoring, and responsible natural resource management.
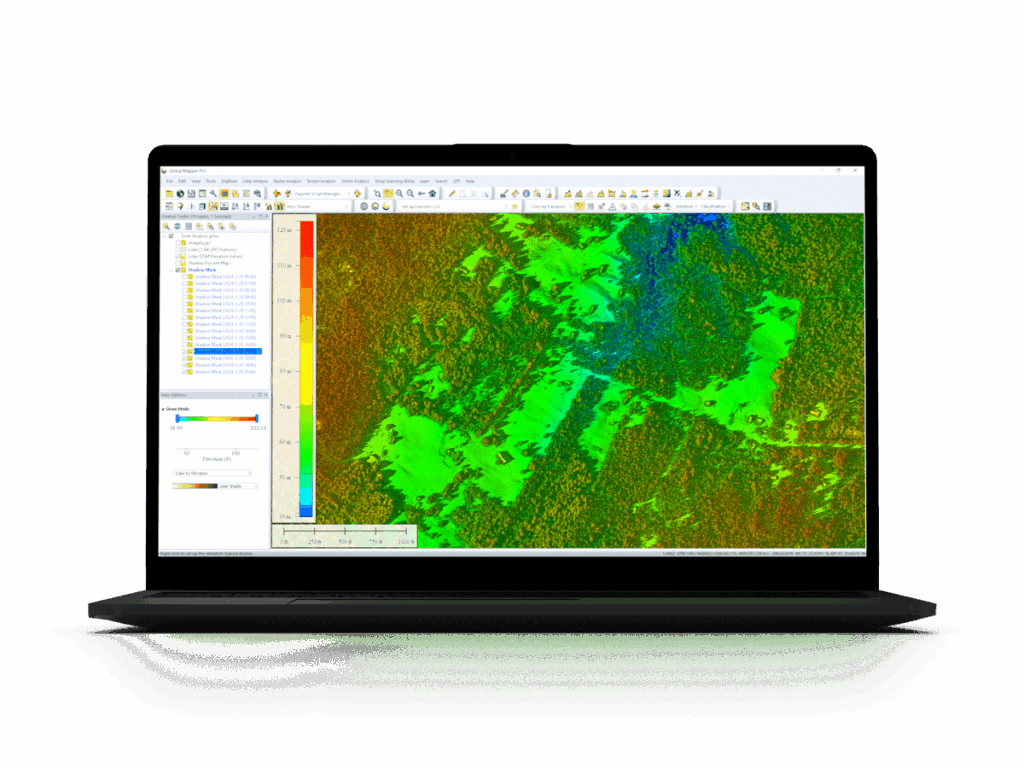
GIS solutions come in desktop, cloud, and SaaS formats, each tailored for different workflows. Today’s users also benefit from extensive geospatial data marketplaces covering almost every industry.
Some of the leading GIS softwares include:
Whether you are a government agency, utility provider, business, or academic institution, GNSS.AE team can help you choose the best GIS tools for your operational needs.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become an essential pillar of modern decision-making. By connecting data with location, GIS enables organisations to analyse patterns, predict outcomes, and design smarter, more sustainable solutions. From urban planning and infrastructure development to environmental monitoring, transportation management, and business strategy, GIS empowers industries to operate with greater precision and agility.
As geospatial data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the value of GIS will only increase. Organisations that adopt advanced geospatial tools gain a significant competitive advantage, reducing operational costs, improving service delivery, mitigating risks and unlocking deeper insights about the world around them.
At GNSS.AE, we are committed to helping businesses, government entities, and professionals harness the full power of GIS. Through tailored solutions, we support our clients in transforming geographic data into actionable intelligence.
Whether you are starting your GIS journey or looking to enhance your existing capabilities, our team is here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us to explore how GIS can elevate your operations and decision-making.