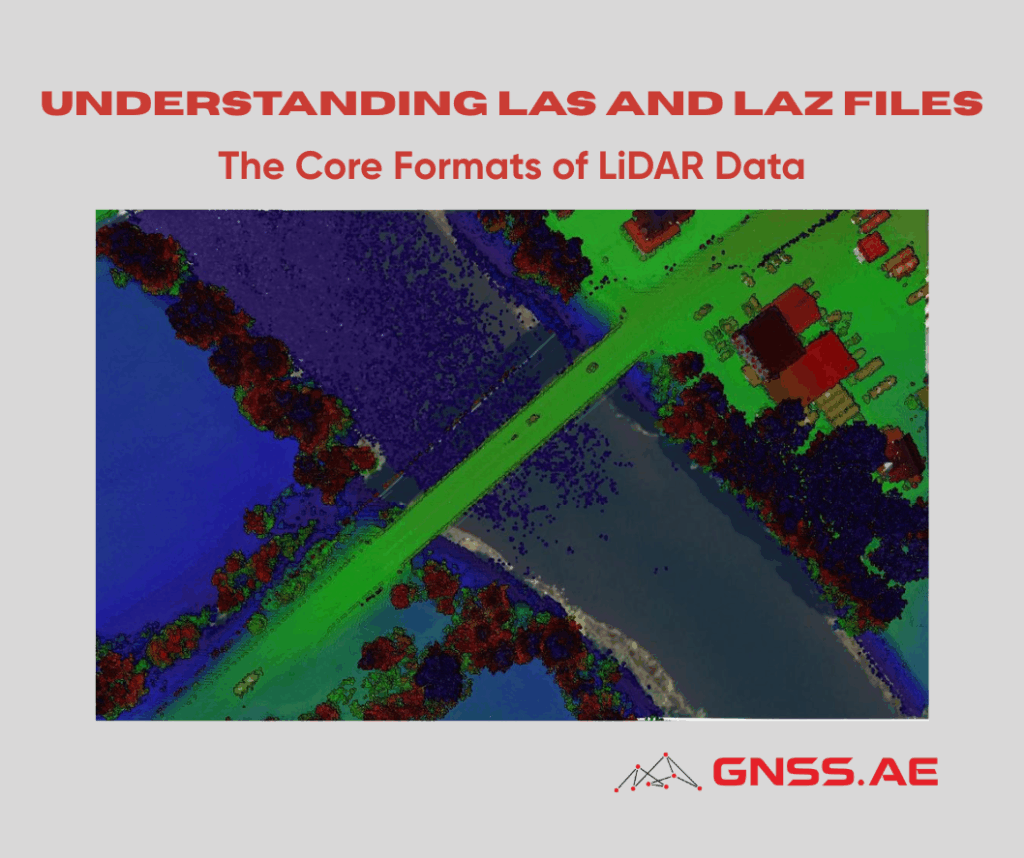
Whether aerial, terrestrial, or underwater — laser scanning technology is becoming an integral part of modern surveying and geospatial workflows. With its growing adoption, specialists increasingly encounter two specific file formats: LAS and LAZ. In this article, we explain what these formats are, where they are used, and why they are essential for working with point cloud data.
LAS and LAZ are binary file formats designed to store and exchange LiDAR point cloud data.
The LAS format (LiDAR Aerial Survey) is the industry standard for storing and transferring laser scanning data obtained from almost any LiDAR sensor. It is widely supported by major geospatial software applications and is used extensively in surveying, mapping, and 3D modeling.
The format was developed in 2003 by the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS) and has since become one of the most recognized standards in the LiDAR data community.
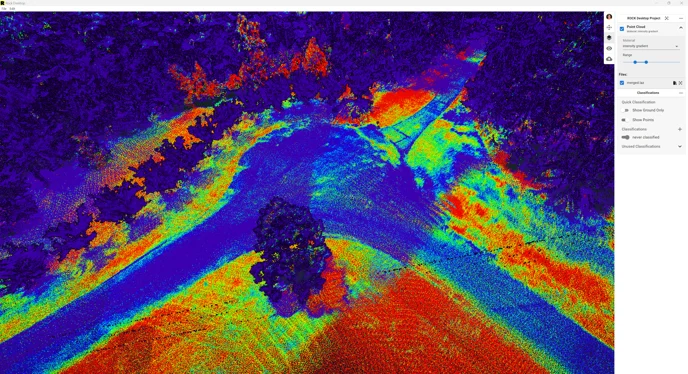
A LAS file stores detailed information about every point in the point cloud, including:
These attributes enable users to visualize and analyze LiDAR data from multiple perspectives, supporting tasks such as terrain modeling, vegetation analysis, and infrastructure mapping.
The most commonly used LAS file versions today are 1.2 and 1.4.
Version 1.4 introduced several important enhancements over earlier versions, including:
The LAS format gained popularity thanks to its:
Additionally, LAS files can be extended with new attributes when needed. Each file includes a header containing metadata such as the coordinate system, date and time of the scan, and the software used for file creation.
LAS files can be generated using various point cloud processing programs.
Introduced in 2007, the LAZ format is an open-source, lossless compression solution for LAS files. It was developed to reduce the storage requirements of LiDAR datasets without compromising data quality.
By compressing a LAS file into LAZ, users can reduce its size by up to 90% while preserving all original information — a crucial advantage when working with large datasets typical in aerial or terrestrial LiDAR projects.
Both LAS and LAZ formats are highly compatible with most LiDAR processing and visualization software used in surveying, mapping, engineering design, forestry, and environmental monitoring.
This broad compatibility ensures that users can exchange, process, and analyze point cloud data efficiently without needing specialized software or additional data conversions.
LAS and LAZ formats have become cornerstones of modern LiDAR workflows. They provide a universal, efficient, and reliable way to store, exchange, and process point cloud data across different industries — from geodesy and civil engineering to environmental analysis and 3D urban modeling.
As laser scanning technologies continue to advance, these formats will remain essential tools for professionals working with spatial data in both traditional and emerging applications.